In the previous two articles, we have discussed signal integrity, crosstalk, crosstalk mechanisms, the parasitic capacitances associated to interconnects, crosstalk noise, crosstalk delay and its effects. In this article, we will discuss the timing window analysis of crosstalk and the prevention techniques of crosstalk.
Timing Window Analysis
Crosstalk timing window analysis is based on the concept that we need to consider a timing window on which the aggressor has an effect on victim net. This analysis method is more accurate and less pessimistic as compare to the infinite arrival window where we assume that aggressor can switch at any time. Figure-1 shows the switching window of a victim net. If the aggressor net switching window overlaps with the switching window of the victim net then only delay of victim cell get affected else it will not get affected.
Here we have shown the out of phase case where delay increases due to the crosstalk effect, but this concept is equally applicable in case of in-phase transition where delay will decrease.
Timing widow concept is also applicable in the crosstalk noise analysis also. In the case of multiple aggressors effect on a victim net, the analysis will be carried out based on the timing widow only. This is a more realistic approach.
Crosstalk prevention techniques
There are various ways to prevent crosstalk, some of the well-known techniques are as follow.
1. Increase the spacing between aggressor and victim net:
Figure-2 shows that by increasing the spacing between aggressor and victim net we are ultimately reducing the coupling capacitance between them as the capacitance is inversely proportional to the distance between them. So by increasing the spacing crosstalk will decrease.
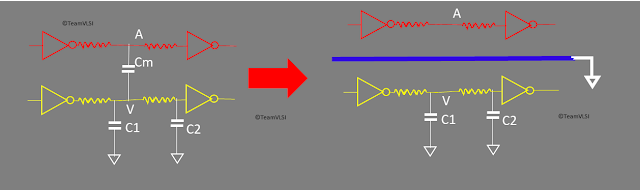
2. Shielding of nets:
Figure-3 shows the shielding technique used to prevent crosstalk. Generally, we insert a shielding net between the victim and the aggressor net. The shielding net is connected to strong VDD or VSS.
By shielding a net the two things will happen, one is the direct coupling capacitance between the aggressor and victim net will vanish and secondly the shielding net will remain at a constant logic so there are no chances of crosstalk.
The above two techniques will prevent the crosstalk but it has an impact on the area. Both techniques will require more area to route them.
3. Upsizing the victim cell:
If we increase the drive strength of the victim cell it will not be easy to affect by the aggressor net.
4. Downsize the aggressor cell:
Higher the drive strength of aggressor cell, higher is the impact of crosstalk on the victim. So by reducing the drive strength we can reduce the crosstalk effect.
Crosstalk timing window analysis is based on the concept that we need to consider a timing window on which the aggressor has an effect on victim net.
Thank you.



No, it won't create glitch on shield net as shield net is strongly connected to VDD/VSS.
Hi, could you please answer a question?
With the shielding nets solution, the shielding nets can be 0 or 1 (constant logic) and the victim nets is switching (L2H or H2L) => create a case as Crosstalk glitch ?
Thank for your article. For convenient case, please send to me via email: tranthingocguong2601@gmail.com
Thank so much 🙂
why we connect shield net to strong vdd/vss?
So that the shield net remain unaffected due to aggressor switching and can protect the victim net.
Ok, I agree with your question but when we shied it with Vdd how can it be? Vss is ground so if any noise occurs in the aggressor net then it will be grounded but if we do shielding with Vdd it is not possible right?
Does shielding the net help in some other issues other than crosstalk ?